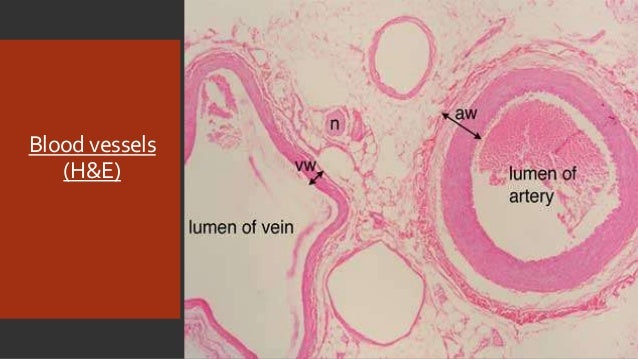
Venules and veins The structure of venules and veins is essentially similar structure to arterioles and arteries In contrast to arteries, the tunica media is considerably thinner and the tunica adventitia may form the thickest wall component Post capillary venules have a particularly important function in inflammatory responses, contributing to fluid leakage and leukocyteInstructions For each histology question, pick the one best answer This histology test bank is also useful for the histology questions on the USMLE (USMLE step 1) 1 Which structure receives blood from the capillary bed?Uniting capillaries drain into veins further from capillary bed tunica media increases Veins same 3 coats as arteries tunica interna and tunica media thinner than companion artery, tunica externa thicker many veins contain valves to prevent back flow Aorta
Blue Histology Vascular System
Artery vein capillary histology
Artery vein capillary histology-Artery and Vein Slide Labeled; This is composed of veins, arteries and capillaries, does not have the same repercussions if it occurs in an artery, vein or capillary The latter are the most expendable, being so narrow that they are usually beyond the reach of the human eye, and their rupture as a whole will produce bruising, but usually not much more In contrast, a cut in the other two can be deadly arteries



Anatomy 15 Virtual Microscopy
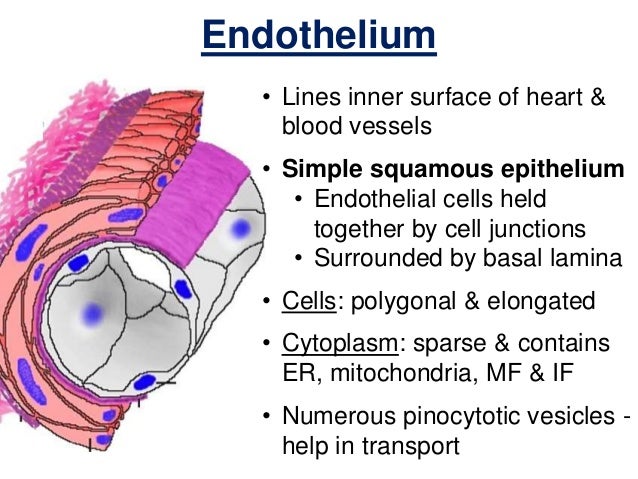
Capillaries have a single layer of flattened endothelial cells, as shown here in the diagram There are no muscular or adventitial layers The thinness of the capillaries helps efficient exchange between the lumen of the capillary and the surrounding tissue Continuous capillaries often have pericytes associated with them (perivascular cells peri is greek for 'around') lie just underneath the Capillary Under Microscope Labeled Histology Of Blood Vessels The renal structures that conduct the essential work of the kidney cannot be seen by the naked eye Artery under microscope labeled The arteries and veins are the plumbing of the body and are responsible for moving blood to and from all of the vital organs This simply involves placing a section of theSlide 303 Artery & vein, Verhoeff stain elastic fibers stain purple View Virtual Slide Slide 304 Femoral artery & vein, canine, van Gieson stain elastic fibers stain brown View Virtual Slide Additional slides (not referenced below, but they show more examples of muscular arteries and veins) Slide 95 Mesentery, H&E View Virtual Slide
Histology of arteries, veins and capillaries (preview) Microscopic Anatomy Kenhub Histology of arteries, veins and capillaries (preview) Microscopic AnatomyHistology hint from Sarah Bellham Elastic arteries also have an internal elastic membrane However, there is so much elastic material in the tunica intima of an elastic artery, that a single, discrete internal elastic membrane is not visible BLOOD VESSELS , , & •AMIR RIFAAT 2 3 major types Arteries Capillaries Veins 2 subtypes Arterioles Venules 60,000 miles or 100,000km of blood vessels 3 • As the heart contracts, it forces blood into the large arteries leaving the ventricles • The blood then move to smaller arteries, finally reaching their smallest branches, the
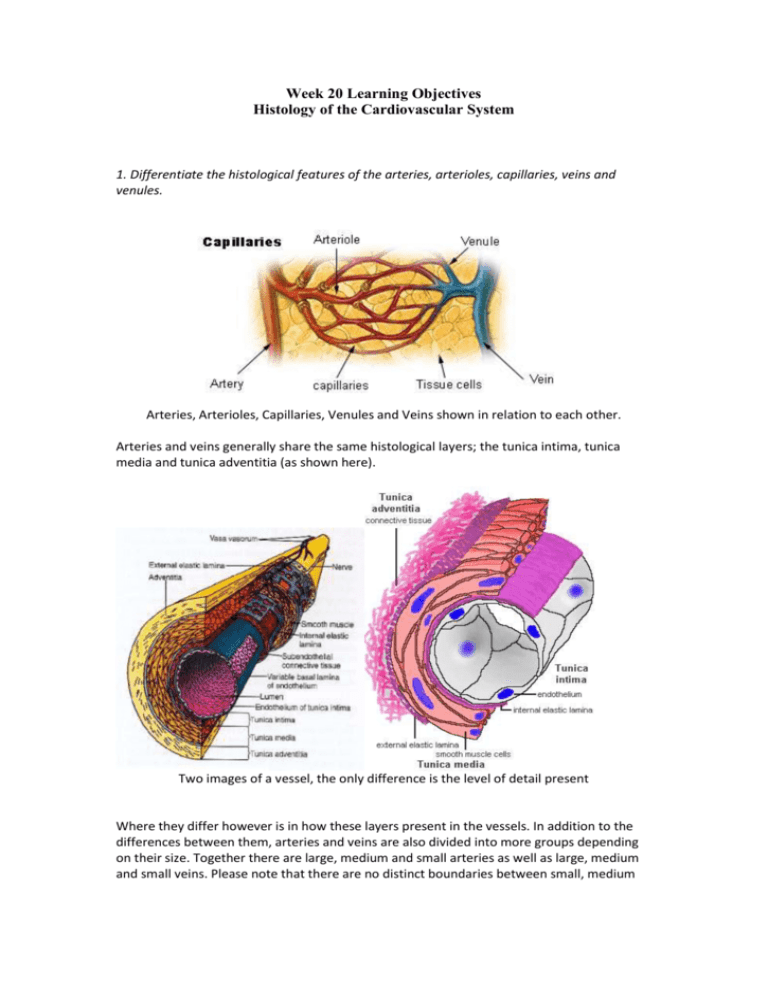
The microarchitecture of the heartarteries, veins, and capillariesis reflected in their functions The close and strikingly obvious correlation between structure and function in the heart and vessels of the blood vascular system greatly simplifies understanding their histologic organization The distribution vessels, the arteries, handle large volumes of blood at high pressure Consequently, one would predict that the arteries Summary Blood vessels are an integral component of the circulatory systemThe five types of blood vessels are (in order of circulation) arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veinsThe primary function of large blood vessels (ie, arteries and veins) is the transport of blood to and from the heart, whereas smaller blood vessels (eg, capillaries) enable substanceBased on their structure and function, blood vessels are classified as either arteries, capillaries, or veins Arteries Arteries carry blood away from the heart Histology hint from Sarah Bellham Learn this definition of artery "arteries carry blood away from the heart" Do not consider oxygenation when classifying a vessel as an artery or vein While most arteries carry




Vessel Comparison Bioninja




Lab 32 Artery Vein Histology Flashcards Quizlet
•Capillaries form networks called capillary bed •Blood flow through the capillary is regulated by precapillary sphincter •Capillaries allow exchange between interstitial fluid and blood by •Active transport •Passive transport •Osmosis, •Diffusion, •Filtration, •Facilitated Transportation CapillariesHepatic arteries > The liver has a dual blood supply The hepatic artery carries oxygenated blood The larger hepatic portal vein supplies a much greater volume of blood that is low in oxygen but high in nutrients;Capillaries are grouped into capillary beds that are filled with blood by arteries and drained by veins A capillary is narrower at its proximal end, where it receives blood from arteries, averaging 5 μm in diameter It widens to about 9 μm in diameter at its distal end, where it meets veins The Three Types of Blood Vessels There are three major types of blood vessels in the human body



Circulatory System The Histology Guide




Histology Of Blood Vessels Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Artery versus Vein Histology;Artery # 9 Large vein Note flattened endothelial cells viewed on their side and on face (flat side of pancake) in arterioles in the iris (left side near the trabecular meshwork of the monkey eye Slide Slide Fattened endothelial cells Iris of monkey eye Anterior chamber Onface view Arteriole Dilator muscle • Slides 226, note that the endocardium Layer of Histology of blood vessels 1 Blood Vessels 2 Objectives • Introduction • Components of circulatory system • Blood vessels – Basic structure • Arteries Elastic & Muscular • Arterioles, Metaarteriole • Capillaries Continuous, Fenestrated, Sinusoidal • Venules, Veins •




Histology Vascular



Chapter 10 Page 1 Histologyolm 4 0
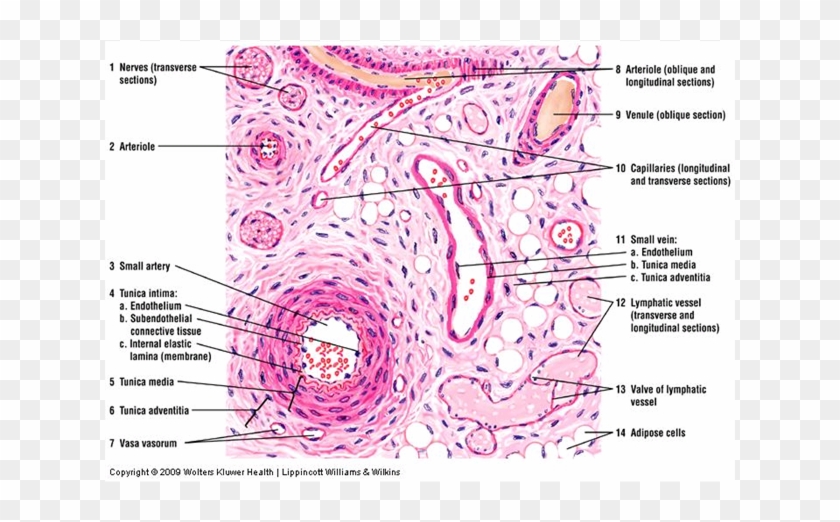
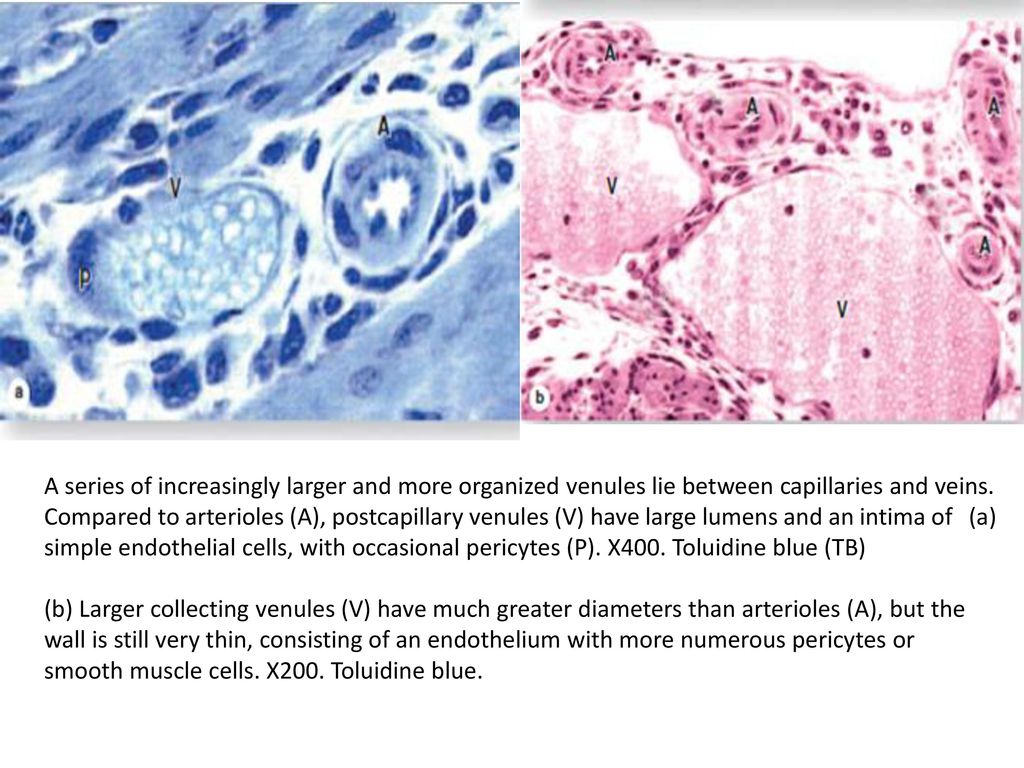
Prior to stage 3, graders were further trained to identify veins by recognizing their origin in vortices within the DCP (characterized as green convergence of capillaries on color depthencoded slabs) and to consider that arteries and veins typically alternate as each vein drains capillary beds perfused by adjacent arteries in stage 3 The training time prior to stage 2 andA capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and having a wall one endothelial cell thick They are the smallest blood vessels in the body they convey blood between the arterioles and venules These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, Continous capillary (histological slide) Veins and derivatives The terminal capillaries coalesce to form postcapillary veins These post capillary veins then unite and form venules, which then progress to larger veins, which will return deoxygenated blood back to the heart Veins possess all three tunics that are found in arteries




Small Arteries Arterioles Slide Wsu 2 052



1
This blood comes directly from capillaryConsequently, arteries tend to maintain their round shape better than veins in histological sections Veins also contain valves to prevent back flow of blood but these are infrequent and are not reliably seen in histological samples Small Artery and Venule Vena Cava This image shows the wall of the vena cava, which is the largest vein in the Elastic type artery has multiple layers of elastic membranes in the tunica media Muscularis type artery as shown has 2 distinct internal and external elastic laminae Sinusoid is a type of capillary and has only a single layer of endothelium without tunica media / adventitia or elastic lamina Comment Here Reference Histologyblood vessels




Histopathology Of Hypertensive Renal Disease Light Micrograph Stock Image Image Of Disease Vessel




Histopathology Of Hypertensive Renal Disease Light Micrograph Stock Photo Image Of Microscopic Histology
This video "Vessels Arteries, Veins & Capillaries" is part of the Lecturio course "Histology" WATCH the complete course on http//lecturio/vesselsovervieVeins same 3 coats as arteries tunica interna and tunica media thinner than companion artery, tunica externa thicker many veins contain valves to prevent back flow Aort There are two main components in the red pulp of spleen histology venous sinuses or venules and splenic cords The splenic sinuses are wide vascular channels that lines with elongated, longitudinally orientedArteries possess the all three basic histological layers of all cardiovascular tissues (See Cardiovascular Histology)The diameter and histological features of arteries transition throughout the cardiovascular system in accordance with their different functionalities, allowing for their categorization into three distinct histofunctional subtypes described further below



Circulatory System The Histology Guide




Bl V
Histology of endocrine part 2 13 terms belen_marie Other Quizlet sets Nervous System III Senses 33 terms gmcelrath14 Child Psych Exam 1 93 termsProducts/Biology/Prepared Slides/Histology/Vascular System SKU PMS1 Artery, vein and capillaries, TS, H&E stain Microscope slide Description;Artery and Vein Under Microscope;
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3613/OgR38mkJaHfLSb8S17ENg_Lymphatic_vessel_of_the_dermis.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
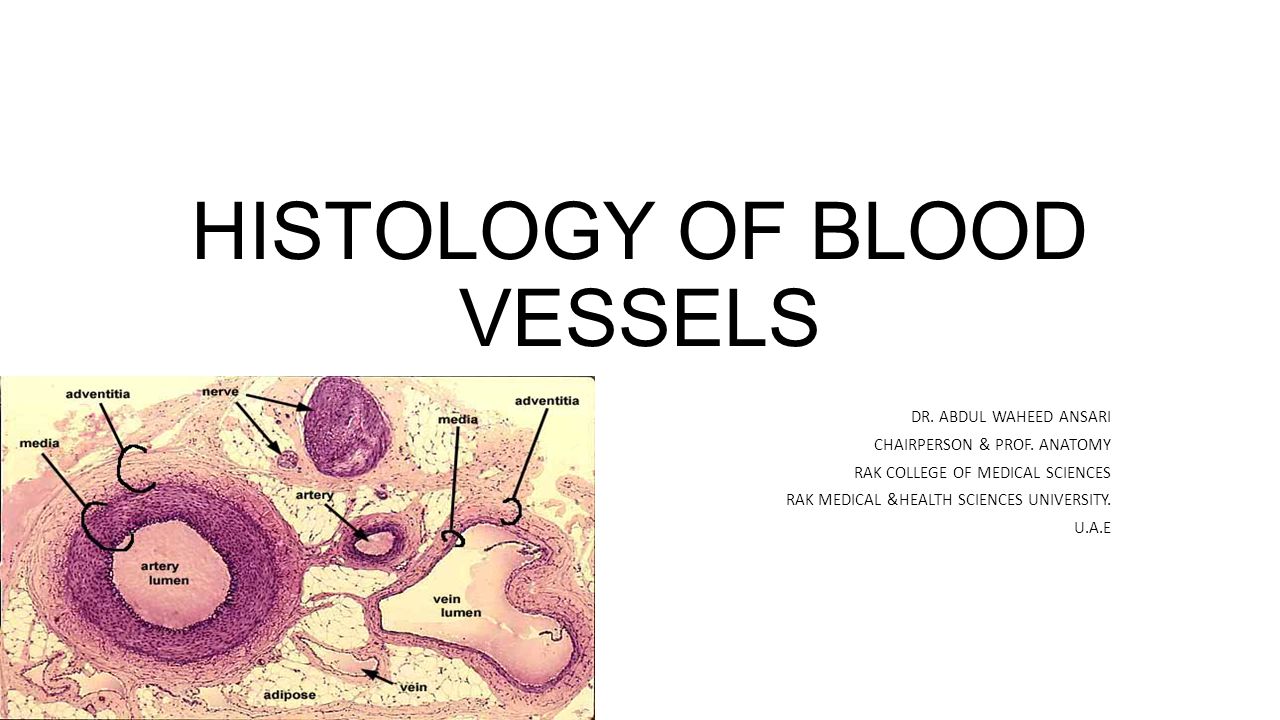



Histology Of Blood Vessels Ppt Video Online Download
Instructions For each histology question, pick the one best answer This histology test bank is also useful for the histology questions on the USMLE (USMLE step 1) Click here for answers and detailed explanations 1 At what level of the vascular tree does gas exchange occur?Histology of arteries and veins STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Robbo1974 PLUS Terms in this set (8) What is the vital functions of arteries and veins All chemical and gaseous exchange between blood and interstitial fluid takes place across capillary walls Cells rely on capillary diffusion to obtain nutrients and oxygen and toThe pulmonary vasculature comprises three anatomic compartments connected in series the arterial tree, an extensive capillary bed, and the venular tree Although, in general, this vasculature is thinwalled, structure is nonetheless complex Contributions to
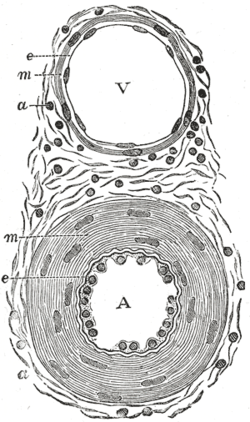



Tunica Media Wikipedia




Arterioles Venules Main Differences Histology Lecturio Youtube
Veins The walls of veins are thinner than the walls of arteries, while their diameter is larger In contrast to arteries, the layering in the wall of veins is not very distinct The tunica intima is very thin Only the largest veins contain an appreciable amount of subendothelial connective tissue Internal and external elastic laminae are absent or very thin The tunica media appears thinnerA Capillary b Arteriole c Venule d Elastic artery e Muscular artery Answer cArteries carry blood away from the heart, regardless of the degree of blood oxygenation Veins carry blood toward the heart Between arteries and veins, there is a network of capillaries that spread inside all organs, reaching practically every cell in the body The thin walls of capillaries allow for the passage of substances between blood and interstitial fluid, surrounding the cells




Histology Vessels



Blood Vessel Histology
A Capillary b Arteriole c Venule d Elastic artery e Muscular artery 2The cardiovascular system transports blood to and from the heart to all tissues of the body Its main function is to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide, nutIn larger arteries, elastic fibers unite to form a lamella which alternate with the layers of muscular fibers These fibers are connected with the membrane of the tunica intima In the largest arteries, there are a few bundles of white connective tissue that are wrapped around the tunica media Tunica adventitia The tunica adventitia is the outer layer of an artery, it surrounds the tunica




Histology Of Arteries Veins And Capillaries Preview Microscopic Anatomy Kenhub Youtube



Histology Of Blood Vessels
Blood is transported in arteries, veins and capillaries Blood is pumped from the heart in the arteries It is returned to the heart in the veins The capillaries connect the two types of bloodThe heart pumps the blood through a series of arteries that branch into smaller and smaller blood vessels that supply the tissues with blood The smallest arteries branch further to become arterioles, which drain the blood into capillaries The capillaries form a network of tiny blood vessels that perfuse the tissueStudy HistologyArteries, Veins and Capillaries flashcards from John Doe's class online, or in Brainscape's iPhone or Android app Learn faster with spaced repetition
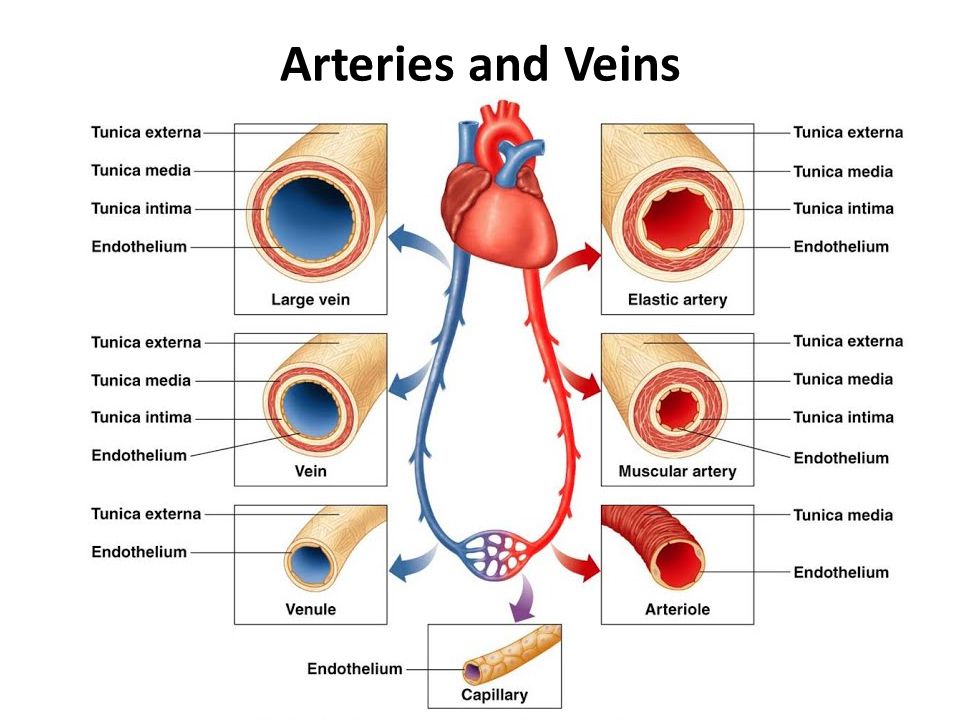



Histology Of Blood Vessels Ppt Video Online Download




Long Answer Question Describe Histological Structure Of Artery Vein And Capillary Biology Shaalaa Com
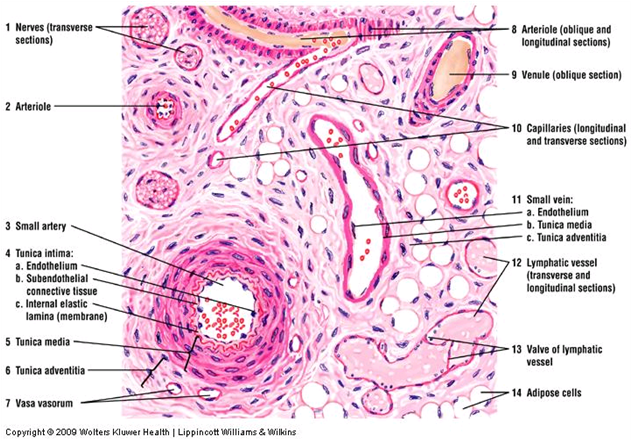
HISTOLOGY LAB VII CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY arteriole artery capillary cardiac muscle endo, myo, and epicardium elastic artery internal and external elastic laminae Purkinje fiber tunica intima, media, and adventitia vas vasi (pl vasa vasorum) vein venule Slide #170 (Artery, vein, and nerve) There are several features that allow one to distinguish between arteriesDescription This slide shows artery, vein and capillaries in a transverse (cross) section, stained with H&E (haematoxylin and eosin) to show nuclei in blue and the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm in pink Qty 1 slide Click to view morePurpose To introduce a simple method for differentiating retinal veins from arteries on optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) Design Crosssectional pilot study Methods Four default en face slabs including color depth encoded, grayscale fullthickness retina, superficial plexus, and deep capillary plexus (DCP) from nine 3×3mm and nine 6×6mm OCTA scans were




Cross Section Of Artery Vein For Fl Youtube
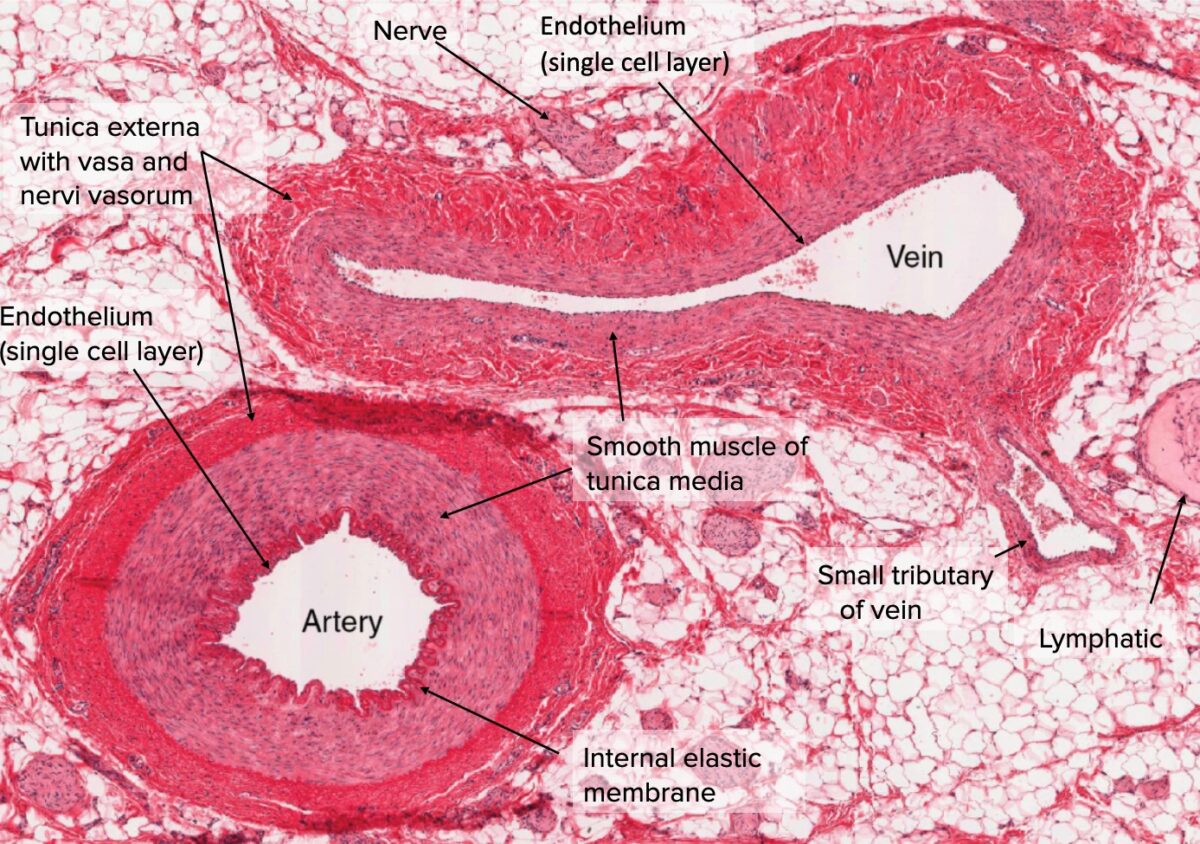



Arteries Concise Medical Knowledge
Passing the capillary bed and draining into a small vein b Arteriovenous anastomoses are small vessels that directly connect arterioles to venules, bypassing the capillary bed They function in thermoregulation and also control blood pressure and flow D Veins conduct blood away from the organs and tissues to the heart and contain about 70% Of the bodÿs total blood volume at anyThe normal flow of blood is as follows artery arteriole capillary post capillary venule vein However, exceptions to this pattern of blood flow exist The phenomenon when a vein is between two capillary beds is called a venous portal system An example of this is the hepatic portal system Another example of a venous portal system is seen in the brain between the hypothalamus and




Lung Tissue Histology Abnormally Located Veins Adjacent To Arteries Download Scientific Diagram
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3607/bxosDBcdwLdq47dXkSy4A_Fenestrated_capillaries.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
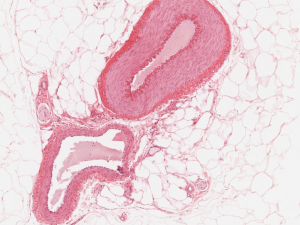



Cardiovascular System Histology



Blue Histology Vascular System
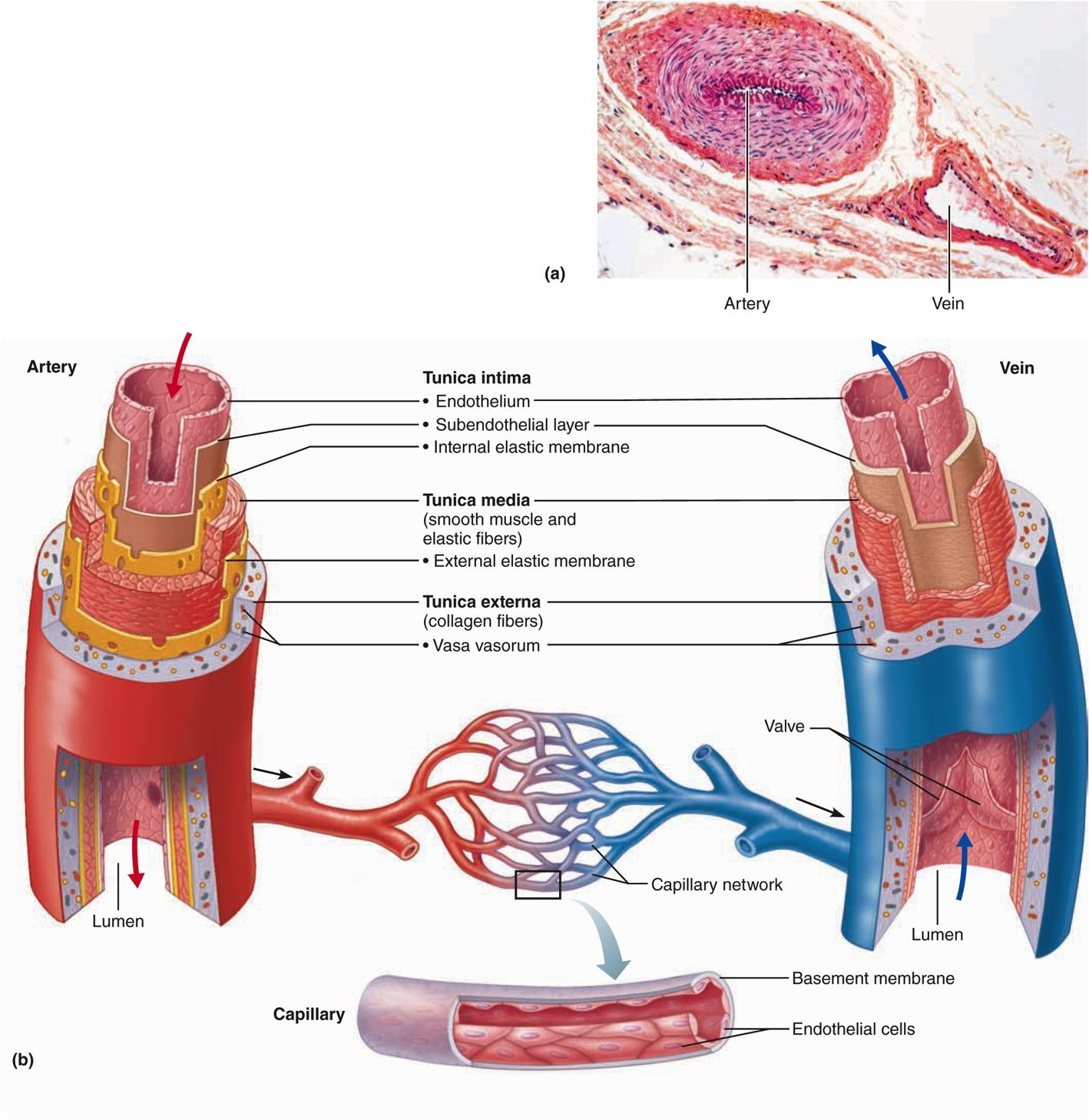



Artery Vein Artery Vein Tunica Intima Endothelium Chegg Com



Blue Histology Vascular System



Histology Laboratory Manual




Vessel Comparison Bioninja



Artery Vein Capillary Elastic Tissue Stain Prepared Microscope Slide
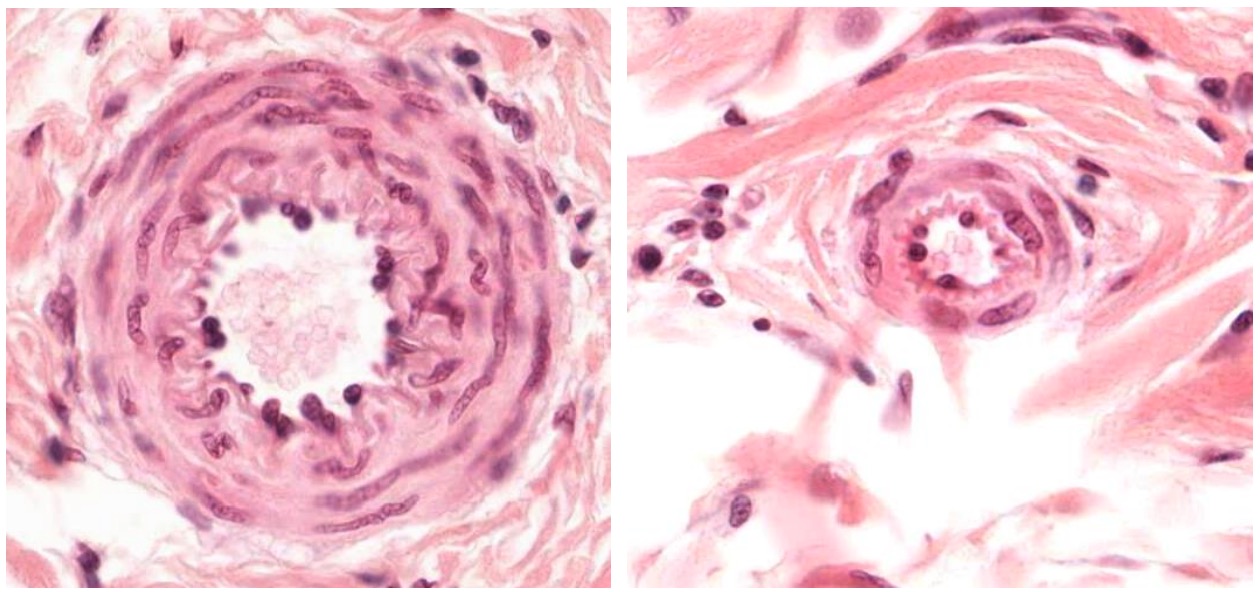



Arteries Concise Medical Knowledge




Animal Organs Cardiovascular System Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology



1



Blood Vessels Veins Arteries Capillaries Types Of Blood Vessels Histology Clipart Pikpng




Anatomy에 있는 핀




Chapter 19 The Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood




Histopathology Of Hypertensive Renal Disease Light Micrograph Stock Photo Image Of Kidney Histology



Circulatory System The Histology Guide



Http Fdjpkc Fudan Edu Cn Upload Article Files 93 8f C0f2beb8f293de4f4a 5b9a2af7 44 4761 9738 C3a5868fc339 Pdf



Blood Vessels Lab
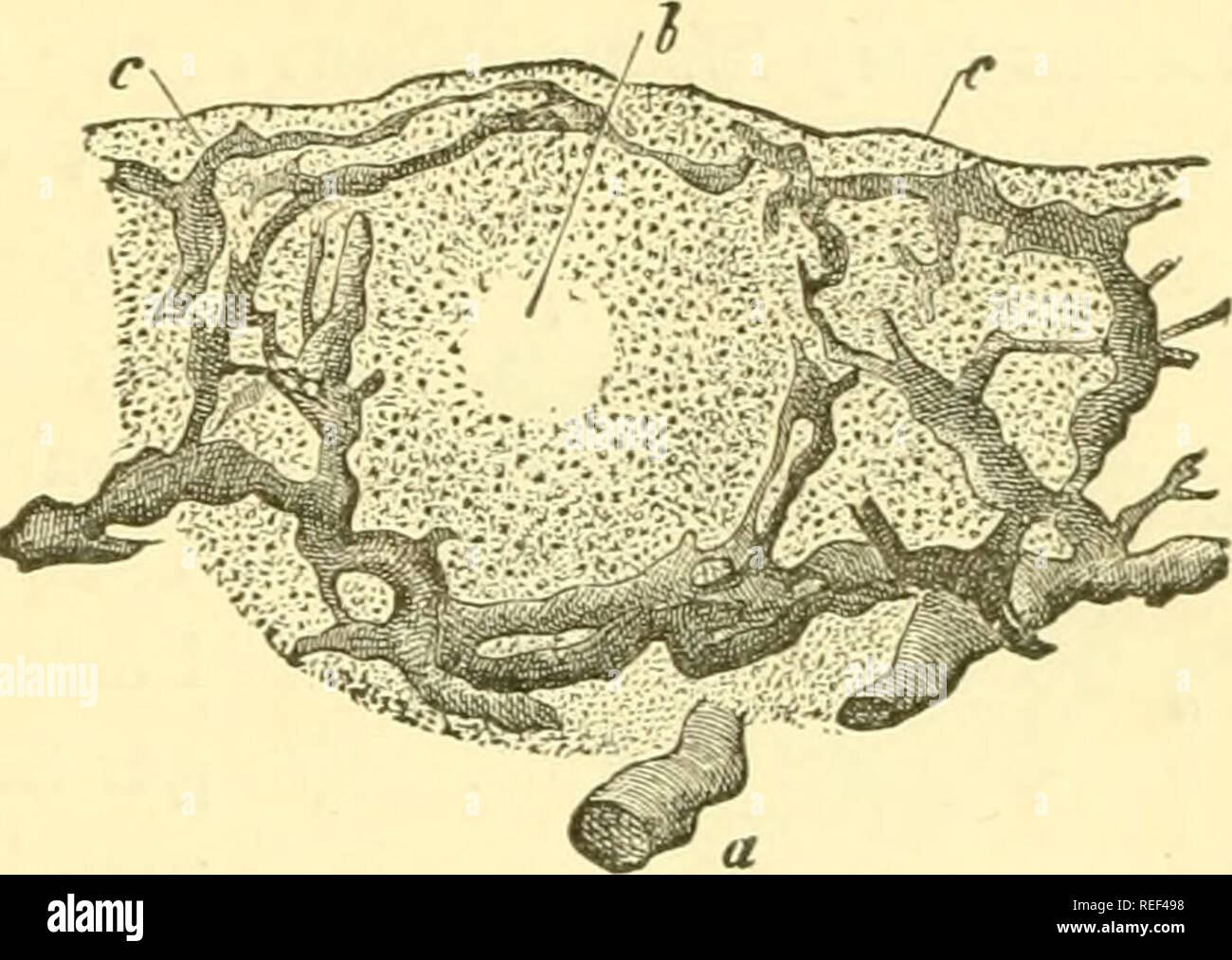



Compendium Of Histology Histology Fig 100 A Colon Papilla Of The Rabbit In Perpendicular Section A Arterial B Venous Trunk Of The Submucous Tissue C Capillary Net Work D Descending



Vetmed Tamu Edu Peer Wp Content Uploads Sites 72 04 9 Blood And Lymph Vessels Pdf



Anatomy 15 Virtual Microscopy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3605/qqhmVxIKd7pxeygeKSM3xw_Muscular_artery_-_Coronary_artery__1_.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub



Semmelweis Hu Anatomia Files 17 09 Blood Vessels 17nov Pdf



Blood Vessels Lab
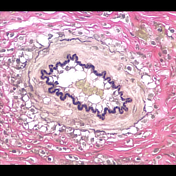



Histology Of Blood Vessels Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
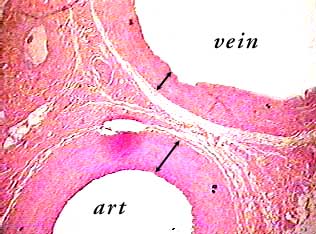



Artery And Vein C S




Histology Of Circulatory System Iii Ppt Download




Blood Vessels Lymphatic Organs Faculty Of Pharmacy 2



Blue Histology Vascular System
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3615/NOpbXd2vHcY0t8xD0mZLQ_Vasa_vasorum.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub



Blood Vessels Veins Arteries Capillaries Types Of Blood Vessels Histology Clipart Large Size Png Image Pikpng




Medical School Cross Section Of An Artery Vein And Capillary Physical Education Lessons Arteries Arteries And Veins
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3603/Tpmr9patPzlfw4MJozUjQ_Elastic_artery_-_Aorta__1_.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub




Arteries
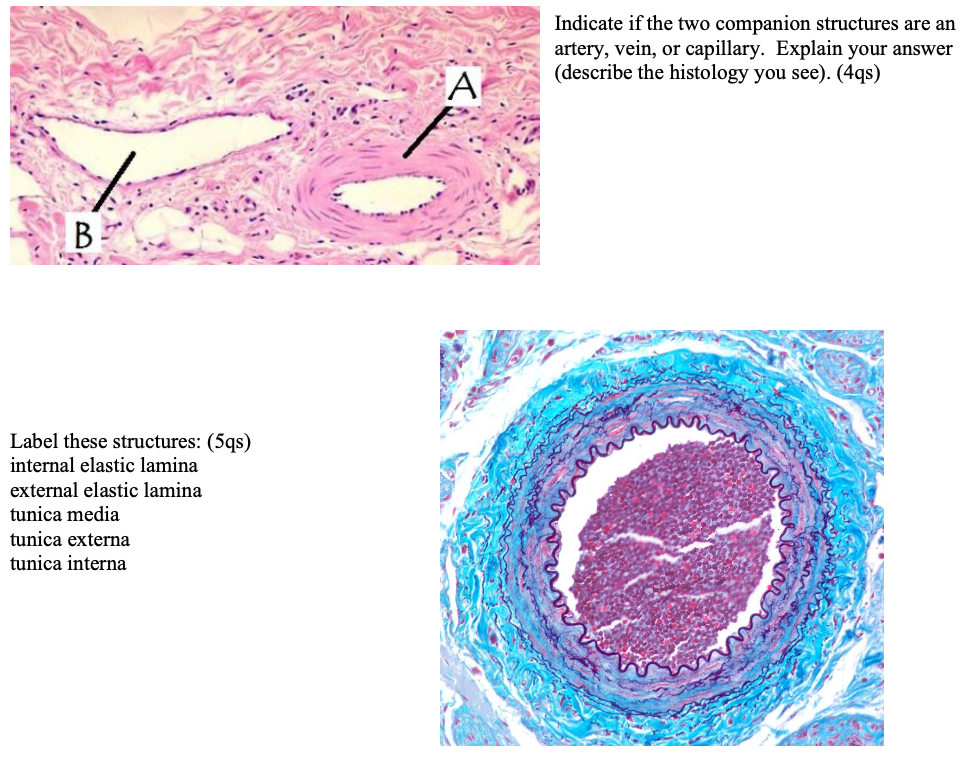



Indicate If The Two Companion Structures Are An Chegg Com




Cardiovascular




Kidney Biopsy Of The Month The Blood Vessels Renal Fellow Network




Artery Vein Capillary Histology




Cardiac Muscle Ppt Video Online Download
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/histology-of-the-vascular-network/qTcfa6edhRn9fZVNzTw_aCakVCMk7M8xtaJDDC6A4w_Artery.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13219/arteries-and-veins.psb_english.jpg)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub




Lung Tissue Histology Abnormally Located Vein Adjacent To Arteries Download Scientific Diagram
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3606/TIdQTQlRbloxtCUKcs2g_Arterioles.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub




Histology Of Artery And Vein Shotgun Histology Youtube



Circulatory System The Histology Guide



Blood Vessels Lab




Blood Vessels Knowledge Amboss




A Histological Overview Of The Lung Tissue With Recognizable Diffuse Download Scientific Diagram




Histopathology Of Hypertensive Renal Disease Light Micrograph Stock Photo Image Of Magnification Microscopy



Circulatory System The Histology Guide



Vessel Lab




Histology Of The Myocardium And Blood Vessels Prof




Histology Vascular



File Wk 1 2




Histology Of The Circulatory System The Cardiovascular System



Blood Vessel Color Images




Histological Findings Of One Of The Stranded Bands 1 Artery 2 Download Scientific Diagram



Blue Histology Vascular System



Blood Vessels Lab



Histolab3a Htm



1
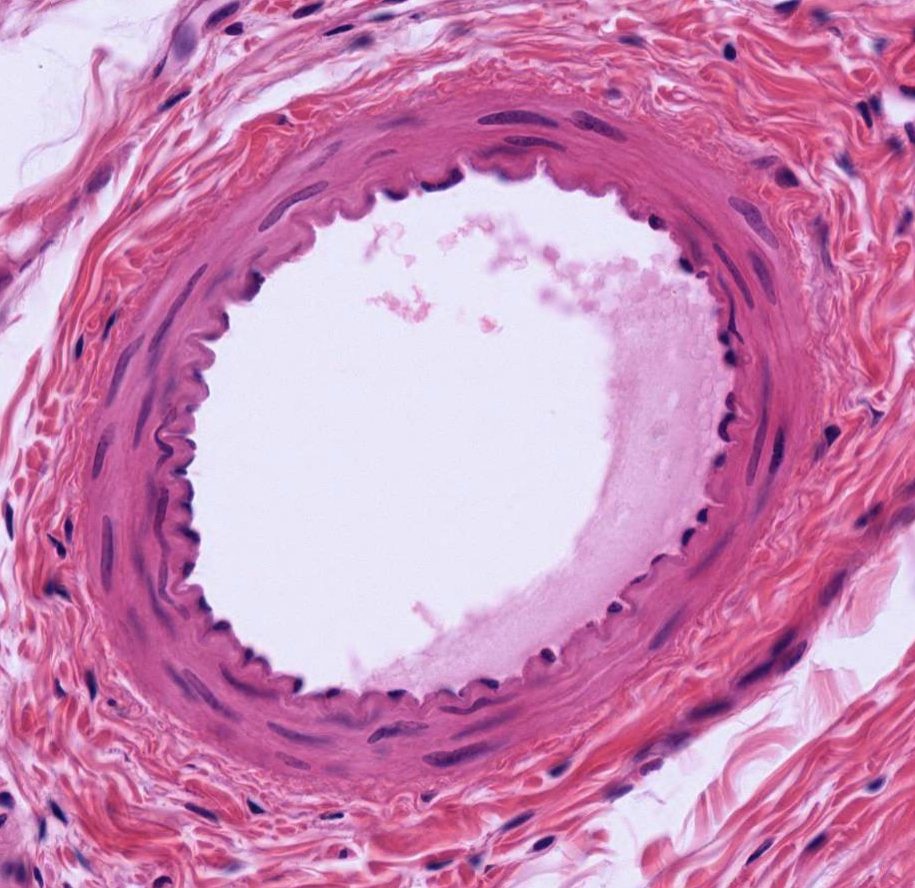



Blood Vessels



Human Structure Virtual Microscopy




Arteries



1



Histology Of Blood Vessels




Arteries



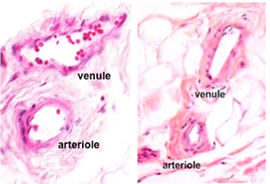
Histology Of Blood Vessels



Http Uoqasim Edu Iq E Learning Lec File Cardiovascular system Pdf



Compendium Of Histology Histology Fig 91 Vascular Net Work Of A Transversely Stri Ated Muscle A Arterial 6 Venous Vessel C D The Capillary Net Work Fig 92 A Pulmonary Alveolus Of The
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3610/5NHWYTWfF0zpaLrwavgwQ_Venule.png)



Blood Vessels Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub



Cardiovascular System Histology Ppt Download



Chapter 10 Page 1 Histologyolm 4 0




Artery Vein And Capillary Cs Mammal Cross Sect Of 3 Vascular Tissues On One Slide H And E Histology Prepared Microscope Slides The Science Shop




Histology Vessels




Histopathology Of Hypertensive Renal Disease Light Micrograph Stock Image Image Of Arterial Artery




Histopathology Of Hypertensive Renal Disease Light Micrograph Stock Image Image Of Micro Tissue



Embryology And Histology Of Bloodvessels



Cardiovascular System Histology



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿